In the field of wireless communication, cell, sector, carrier frequency and carrier are the four basic concepts. They play an important role in cellular networks, affecting network performance, coverage and capacity.
The difference between cell and sector
- Cell:
A cell is an area of a wireless communication network that is covered by a Base Station. It is the basic unit of the cellular network, providing wireless signal coverage and services to users. The characteristics of the community are as follows: - (1) Uniqueness: Each cell has a unique identifier to facilitate network identification and management.
(2) The size is different: the size of the cell depends on the antenna height of the base station, the transmission power and the terrain and other factors.
(3) Coverage: The coverage of the cell can range from several hundred meters to several kilometers.
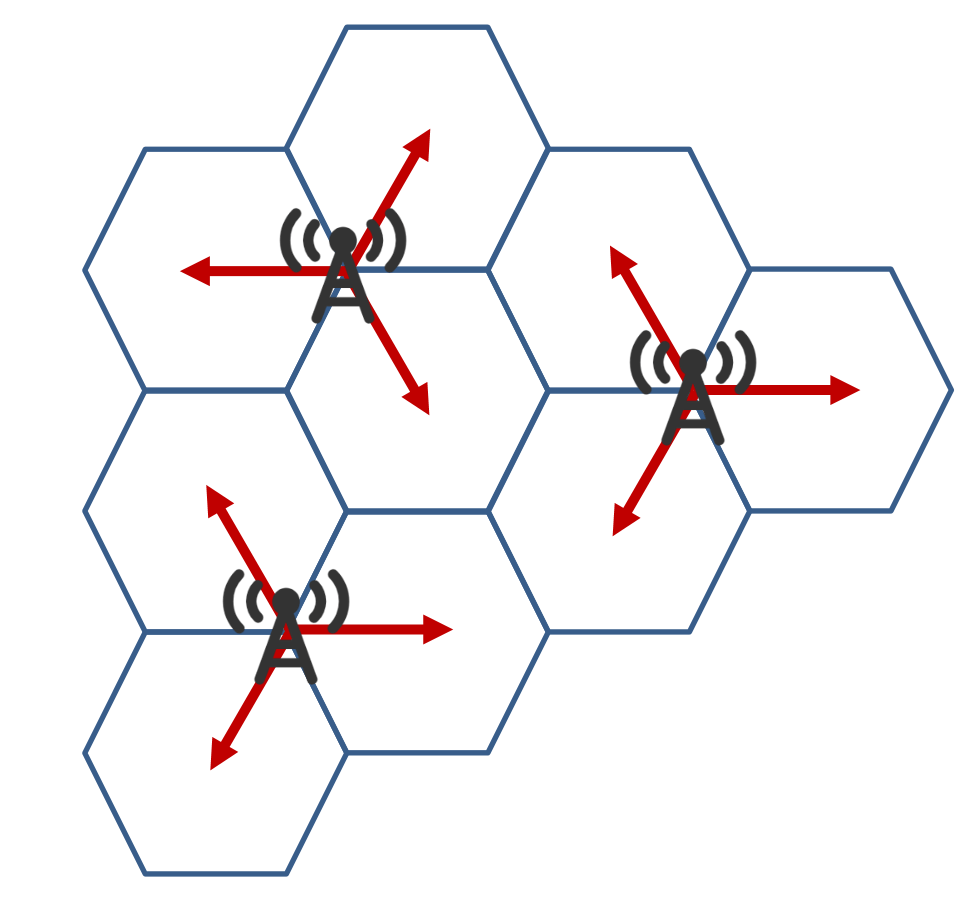
Sector:
A sector is a cell that is further divided into sections, usually by means of a directional antenna. The characteristics of sectors are as follows:
(1) Directionality: Each sector has a specific coverage direction, usually 120 degrees or 60 degrees.
(2) Improve frequency reuse rate: By dividing sectors, the interference between adjacent cells can be reduced and the frequency reuse rate can be improved.
(3) Increase network capacity: The division of sectors helps to improve the capacity of the network and meet the needs of more users.
Difference summary: The cell is the area covered by the base station, and the sector is a directional coverage area within the cell. The size and shape of the cell are relatively fixed, while the sector can be adjusted according to actual needs.
The difference between carrier frequency and carrier
- Carrier Frequency:
Carrier frequency refers to the radio frequency used to transmit the signal. In wireless communication, carrier frequency allocation and use has the following characteristics:
(1) Frequency allocation: Different networks and services use different carrier frequencies, such as 900 MHz or 1800 MHz carrier frequencies for GSM networks.
(2) Channel division: the carrier frequency is divided into multiple channels, each channel is used to transmit a signal.
(3) Unit: The unit of the carrier frequency is Hertz (Hz), indicating the number of vibrations per second. - Carrier Wave:
A carrier wave is an unmodulated radio wave whose frequency carries information during modulation. Carrier characteristics are as follows:
(1) Modulation process: the carrier carries sound, data and other information in the modulation process.
(2) Single frequency: the carrier itself is a sine wave of a single frequency.
(3) Information transmission: By changing the amplitude, frequency or phase of the carrier, information can be encoded on the carrier.
The carrier frequency is the specific frequency used to transmit a signal, while the carrier is the radio wave that carries information during modulation. The carrier frequency is the frequency attribute of the carrier, and the carrier is the concrete realization of the carrier frequency.